Blockchain technology has revolutionized digital transactions, allowing users to exchange assets securely without intermediaries. This system, built on cryptographic principles, enables peer-to-peer transfers with the help of digital wallets and a pair of cryptographic keys. Here, we’ll explore the mechanics of blockchain transactions and how they ensure security and efficiency.
The Process of Sending a Blockchain Transaction
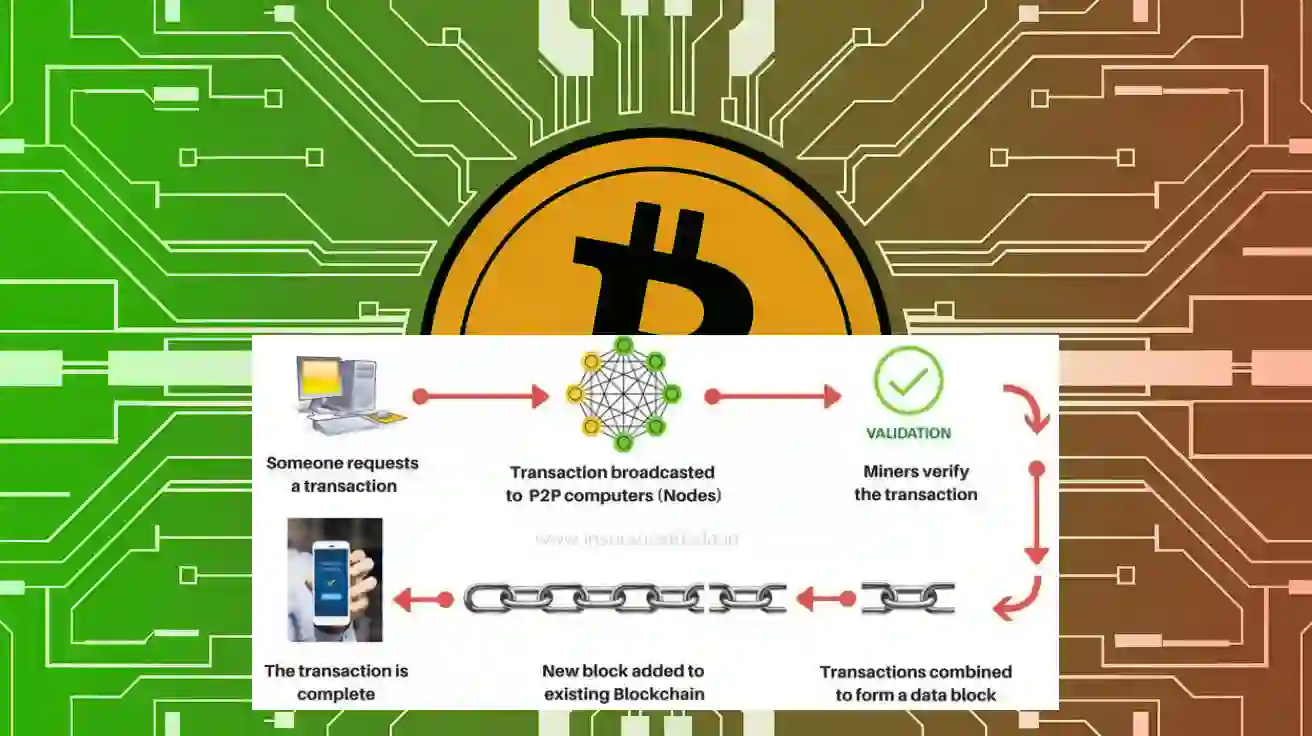
Unlike traditional financial transactions that rely on banks or third parties, blockchain transactions follow a decentralized process. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Obtaining Keys – To initiate a transaction, users need two cryptographic keys: a public key (shared with others) and a private key (kept secret). These keys act as digital signatures to verify transactions.
- Transaction Request – A user requests to send cryptocurrency or digital assets using blockchain software, typically through a digital wallet.
- Validation by Nodes – The blockchain network’s nodes examine the ledger to ensure the sender has sufficient funds and has not already spent the assets in question.
- Transaction Confirmation – If the transaction is valid, it gets added to a block along with other transactions awaiting confirmation.
- Finalizing the Transaction – Once verified by network nodes (miners or validators), the transaction becomes immutable, meaning it cannot be altered or reversed.
Public and Private Keys: The Backbone of Blockchain Security
Blockchain transactions rely on public and private keys to ensure security and authenticity. These keys are lengthy alphanumeric codes generated through cryptographic algorithms:
- Public Key: This is a user’s receiving address, similar to an email address, that can be shared with others for transactions.
- Private Key: This acts as a digital signature, proving ownership of the assets and authorizing transactions. It must be kept secure because losing it means losing access to funds.
A unique feature of blockchain cryptography is that the public key can be mathematically derived from the private key, but the private key cannot be reverse-engineered from the public key. This ensures security while enabling seamless transactions.
Fun Fact:
An estimated 4 million Bitcoins have been permanently lost due to misplaced private keys, amounting to nearly 25% of all Bitcoin in circulation.
Understanding Crypto Wallets
A cryptocurrency wallet is essential for interacting with blockchain networks. Unlike a physical wallet that holds cash, a crypto wallet stores cryptographic keys and facilitates transactions. Wallets come in different forms:
- Software Wallets: Applications on desktops, smartphones, or web browsers that provide convenient access to digital assets.
- Hardware Wallets: Physical devices that store private keys offline, offering enhanced security against hacking.
- Paper Wallets: Physical printouts of public and private keys, used as a cold storage method.
Beyond Currency: Blockchain’s Versatile Applications
While cryptocurrencies are the most well-known use of blockchain transactions, the technology can support various applications, including:
- Smart Contracts – Self-executing agreements programmed to trigger actions when predefined conditions are met.
- Digital Records – Secure storage for documents like birth certificates, land titles, and academic credentials.
- Media and Art – Blockchain facilitates digital ownership of music, movies, and artwork through NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens).
The Future of Blockchain Transactions
Blockchain’s decentralized nature offers significant advantages by eliminating middlemen and enabling secure, trustless transactions. As technology evolves, blockchain is expected to play a pivotal role in industries ranging from finance to healthcare and beyond. By enhancing transaction speed, reducing costs, and improving security, blockchain is reshaping the future of digital exchanges worldwide.
With continuous innovation, the possibilities for blockchain technology are limitless, making it one of the most transformative advancements in modern finance and beyond.